This study is to identify the positive association of food quality, restaurant service quality, physical environment quality, and customer satisfaction with revisit intention of customers at fast food restaurants. Additionally, word of mouth is investigated as moderator on the relationship of customer satisfaction with revisit intentions of customers at fast food restaurants. Data were collected through a questionnaire survey from 433 customers of fast food restaurants through convenience sampling. Hypotheses of proposed model were tested using structural equation modeling with partial least squares SEM-PLS in SMART PLS 3. The results confirmed the positive association of food quality, restaurant service quality, physical environment quality, and customer satisfaction with revisit intentions of customers at fast food restaurants. However, word of mouth does not positively moderate the relationship of customer satisfaction with revisit intentions of customers at fast food restaurants. This study emphasizes the importance of revisit intention as a vital behavioral reaction in fast food restaurants. This study reveals revisit intention’s positive association with food quality, restaurant service quality, physical environment quality, and customer satisfaction based on stimulus-organism-response (S-O-R) theory. Furthermore, it is identified that social conformity theory does not hold its assumption when consumers experience quality and they are satisfied because word of mouth does not moderate the relationship of customer satisfaction with revisit intention of customer.
Hospitality industry is observing diversified changes in highly competitive environment for restaurants [1]. Consumers are becoming conscious of food quality (FQ), restaurant service quality (RSQ), and physical environment quality (PEQ) of the fast food restaurants. Consumers switch easily in case of just one evasive experience [2, 3]. Fast food restaurants must attract new customers and retain the existing customers. There is a growing trend in Pakistani culture to dine out at fast food restaurants with family, friends, and colleagues [4]. Restaurants focus to provide a dining experience by combining tangible and intangible essentials [5]. Decisive objective is to achieve customer satisfaction (CS), word of mouth (WOM), and future revisit intention (RVI) at fast food restaurant.
Restaurants differ in offerings, appearance, service models, and cuisines; this classifies restaurants as downscale and upscale [6, 7]. Revisit intention is the willingness of a consumer to revisit a place due to satisfactory experience. Customer satisfaction generates a probability to revisit in presence or absence of an affirmative attitude toward the restaurant [8]. Revisit intention is a substantial topic in hospitality research [8,9,10]. To date there has been little agreement on that word of mouth can affect revisit intention after experience of customer satisfaction. For instance, when a customer is satisfied at a fast food restaurant experience, however, the customer’s family and friends do not share the same satisfying experience. Will this word of mouth affect the customer’s revisit intention? Food quality is acknowledged as a basic component of the restaurant’s overall experience to affect consumer revisit intention. Fast food quality is substantially associated with customer satisfaction and it is an important predictor of behavioral intention [11]. Service quality is an essential factor to produce consumers’ revisit intentions [12]. Furthermore, physical environment quality affects behavior of consumers at restaurants, hotels, hospitals, retail stores, and banks [13]. Physical environment quality is a precursor of customer satisfaction [9]. This suggests that customer satisfaction is associated with fast food quality, restaurant service quality, physical environment quality, and revisit intention.
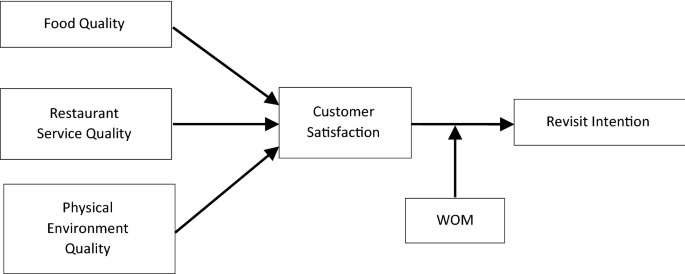
This study is to investigate the association of fast food quality, restaurant service quality, physical environment quality with customer’s revisit intention through mediation of customer satisfaction using S-O-R theory and moderation of word of mouth on the relationship of customer satisfaction with revisit intention based on social conformity theory. This study empirically tests a conceptual research framework based on S-O-R and social conformity theory adding value to the knowledge. Objectives of the study are given below.
Furthermore, little empirical evidence is present about customer satisfaction with respect to fast food restaurant service quality [14]. Customer satisfaction is a post-consumption assessment in service industry. Customer satisfaction acts as the feedback mechanism to boost consumer experience [15]. Customer satisfaction brings competitive advantage to the firm and produces positive behavioral revisit intention [16]. Marketing literature emphasizes customer satisfaction in anticipation of positive word of mouth, revisit intention, and revisit behavior [5]. Behavioral intention is assessed through positive WOM, and it is important in service industry [15], whereas social influence in shape of WOM affects the behavior of individuals toward conformity leading to a driving effect based on social conformity theory [17].
Food quality plays a central role in the restaurant industry. Food quality is essential to satisfy consumer needs. Food quality is a substantial condition to fulfill the needs and expectations of the consumer [18]. Food quality is acknowledged as a basic component of the restaurant’s overall experience. Food quality is a restaurant selection’s most important factor, and it is considerably related to customer satisfaction [11]. Food quality affects customer loyalty, and customer assesses the restaurant on the basis of food quality [19]. Food quality entails food taste, presentation, temperature, freshness, nutrition, and menu variety. Food quality influences customers’ decisions to revisit the restaurant [20]. Academic curiosity is increasing in the restaurant’s menus, as variety of menu items is considered the critical characteristic of food quality [11]. Taste is sensual characteristic of food. Taste is assessed after consumption. Nonetheless, customers foresee taste before consumption through price, quality, food labels, and brand name. Taste of food is important to accomplish customer satisfaction. Presentation of food enhances dining customer satisfaction [21, 22]. Customer’s concerns of healthy food substantially affect customer’s expectations and choice of a restaurant [23]. Freshness is assessed with the aroma, juiciness, crispness, and fresh posture of the food. Food quality enhances customer satisfaction [24].
Quality as a construct is projected by Juran and Deming [25, 26]. Service quality is comparatively a contemporary concept. Service quality assesses the excellence of brands in industry of travel, retail, hotel, airline, and restaurant [27]. Restaurant service quality affects dining experiences of customers. Service quality creates first impression on consumers and affects consumers’ perception of quality [28]. Service industry provides good service quality to the customers to attain sustainable competitive advantage. Customer satisfaction depends on quality of service at the restaurant [29]. Service quality entails price, friendliness, cleanliness, care, diversity, speed of service, and food consistency according to menu. Customer satisfaction also depends on communication between restaurant’s personnel and the customers [30]. Consumer’s evaluation of service quality is affected by level of friendliness and care. Service quality leads to positive word of mouth, customer satisfaction, better corporate image, attraction for the new customers, increase revisits, and amplified business performance. Service quality increases revisits and behavioral intentions of customers in hospitality industry [12].
PEQ is a setting to provide products and services in a restaurant. Physical environment quality contains artifacts, decor, spatial layout, and ambient conditions in a restaurant. Customers desire dining experience to be pleasing; thus, they look for a physical environment quality [31]. Physical environment quality satisfies and attracts new customers. PEQ increases financial performance, and it creates memorable experience for the customers [9]. Consumers perceive the quality of a restaurant based on cleanliness, quirky, comfortable welcoming, physical environment quality, and other amenities that create the ambiance [32]. Effect of physical environment quality on behaviors is visible in service businesses such as restaurants, hotels, hospitals, retail stores, and banks [33]. Physical environment quality is an antecedent of customer satisfaction [34]. Thus, restaurants need to create attractive and distinctive physical environment quality.
Customer satisfaction contains the feelings of pleasure and well-being. Customer satisfaction develops from gaining what customer expects from the service. Customer satisfaction is broadly investigated in consumer behavior and social psychology. Customer satisfaction is described “as the customer’s subjective assessment of the consumption experience, grounded on certain associations between the perceptions of customer and objective characteristics of the product” [35]. Customer satisfaction is the extent to which an experience of consumption brings good feelings. Customer satisfaction is stated as “a comparison of the level of product or service performance, quality, or other outcomes perceived by the consumer with an evaluative standard” [36]. Customer satisfaction constructs as a customer’s wholesome evaluation of an experience. Customer satisfaction is a reaction of fulfilling customer’s needs.
Customer satisfaction brings escalated repeat purchase behavior and intention to refer [37]. Dissatisfied consumers are uncertain to return to the place [38]. Satisfactory restaurant experience can enhance revisit intention of the consumer. Positive WOM is generated when customers are not only satisfied with the brand but they demand superior core offering and high level of service [15].
Word of mouth is described as “person-to-person, oral communication between a communicator and receiver which is perceived as a non-commercial message” [39]. WOM is also defined as “the informal positive or negative communication by customers on the objectively existing and/or subjectively perceived characteristics of the products or services” [40]. Moreover, [41] defines it as “an informal person to person communication between a perceived non-commercial communicator and a receiver regarding a brand, a product, an organization or a service”. WOM is described as a positive or negative statement made by probable, actual or former customers about a product or a company, which is made available through offline or online channels [42, 43]. WOM is an important and frequent sensation; it is known for long time that people habitually exchange their experiences of consumptions with others. Consumers complain about bad hotel stays, talk about new shoes, share info about the finest way of getting out tough stains, spread word about experience of products, services, companies, restaurants, and stores. Social talks made more than 3.3 billion of brand impressions per day [44].
WOM has substantial impact on consumer’s purchasing decision; therefore, a vital marketing strategy is to initiate positive WOM [45]. However, negative WOM is more informative and diagnostic where customers express their dissatisfaction [38]. Word of mouth communications are more informative than traditional marketing communications in service sector. WOM is more credible than advertisement when it is from friends and family [46]. WOM is a vital influencer in purchase intention. WOM escalates affection that enhances commitment of consumer purchase intention. WOM is generated before or after the purchase. WOM helps the consumers to acquire more knowledge for the product and to reduce the perceived risk [47]. WOM in the dining experience is very important. People tend to follow their peers’ opinions when they are to dine out.
To predicting and to explain human behavior is the key determination of consumer behavior research. Consumer needs differ and emerge frequently with diverse outlooks. Revisit intention is to endorse “visitors being willing to revisit the similar place, for satisfactory experiences, and suggest the place to friends to develop the loyalty” [48]. Consumer forms an attitude toward the service provider based on the experience of service. This attitude can be steady dislike or like of the service. This is linked to the consumer’s intention to re-patronize the service and to start WOM. Repurchase intention is at the core of customer loyalty and commitment. Repurchase intention is a significant part of behavioral and attitudinal constructs. Revisit intention is described as optimistic probability to revisit the restaurant. Revisit intention is the willingness of a consumer to visit the restaurant again. Furthermore, the ease of visitors, transportation in destination, entertainment, hospitability, and service satisfaction influence visitor’s revisit intention.
Consumer behavior encircles the upcoming behavioral intention and post-visit evaluation. Post-visit evaluation covers perceived quality, experience, value, and the satisfaction. Restaurant managers are interested to understand the factors of consumer revisit intention, as it is cost effective to retain the existing customers in comparison with attract new customers [49]. Substantial consideration is prevailing in literature for the relationship among quality attributes, customer satisfaction, and revisit intention. There is a positive association between customer satisfaction and revisit intention. Indifferent consumer, accessibility of competitive alternatives and low switching cost can end up in a state where satisfied consumers defect to other options [2]. Consumer behavior varies for choice of place to visit, assessments, and behavioral intentions [50]. The assessments are about the significance perceived by regular customers’ satisfactions. Whereas, future behavioral intentions point to the consumer’s willingness to revisit the similar place and suggest it to the others [51].
S-O-R model is primarily established on the traditional stimulus–response theory. This theory explicates individual’s behavior as learned response to external stimuli. The theory is questioned for oversimplifying ancestries of the behaviors and ignoring one’s mental state. [52] extended the S-O-R model through integrating the notion of organism between stimulus and response. S-O-R concept is embraced to reveal individual’s affective and cognitive conditions before the response behavior [53]. S-O-R framework considers that environment comprises stimuli (S) leading changes to the individual’s internal conditions called organism (O), further leading to responses (R) [52]. In S-O-R model, the stimuli comprise of various components of physical environment quality, organism indicates to internal structures and processes bridging between stimuli and final responses or actions of a consumer [9]. Behavioral responses of an individual in a physical environment quality are directly influenced by the physical environment quality stimulus [54]. S-O-R framework is implemented in diverse service contexts to examine how physical environment quality affects customer’s emotion and behavior [55]. The effect of stimulation in an online shopping environment on impulsive purchase is investigated through S-O-R framework [56]. The effects of background music, on consumers’ affect and cognition, and psychological responses influence behavioral intentions [57]. Perceived flow and website quality toward customer satisfaction affect purchase intention in hotel website based on S-O-R framework [58]. Therefore, this study conceptualizes food quality, restaurant service quality, and physical environment quality as stimuli; customer satisfaction as organism; and revisit intention as response.
Moreover, social conformity theory (SCT) is to support the logical presence of WOM in the conceptual framework as a moderator on the relationship of customer satisfaction and revisit intention. Social conformity influences individual’s attitudes, beliefs and behaviors leading to a herding effect [17, 59]. Thus, social influence (WOM) moderates the relationship of customer satisfaction and revisit intention. Following hypotheses are postulated, see Fig. 1.

Food quality is positively associated with customer satisfaction in fast food restaurant.
Restaurant service quality is positively associated with customer satisfaction in fast food restaurant.